Let me hit you with a question—what do you really know about avian flu? If your answer is "not much," you're not alone. Avian flu, or bird flu as it's casually called, has been making headlines recently, and for good reason. It's not just a virus that affects birds; it has the potential to impact humans too. So, buckle up because we're diving deep into this topic, and I promise to make it as straightforward and engaging as possible.
Now, before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let's clear the air. Avian flu is no joke. It's a highly contagious disease that primarily affects birds, but it has been known to jump species and infect humans under certain circumstances. This isn't just about chickens or ducks; it's a global health concern that demands our attention.
As we unravel the layers of avian flu, you'll discover everything from its origins to how it spreads, its impact on both animals and humans, and most importantly, what you can do to protect yourself and your loved ones. So, whether you're a bird enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or just someone curious about the world around you, this article is for you. Let's get started, shall we?
Read also:Why Corinthians Is More Than Just A Football Club A Deep Dive
Daftar Isi
- What is Avian Flu?
- History of Avian Flu
- How Does Avian Flu Spread?
- Symptoms of Avian Flu
- Avian Flu in Humans
- Prevention and Control
- Economic Impact
- Global Efforts to Combat Avian Flu
- Recent Outbreaks
- Conclusion
What is Avian Flu?
Alright, let's start with the basics. Avian flu, or bird flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza A viruses. These viruses primarily affect birds, both domestic and wild. Now, here's the kicker—some strains of avian flu can jump from birds to humans, and that's where things get serious.
There are different subtypes of avian flu, but the ones that cause the most concern are H5N1, H7N9, and H5N6. These strains have shown the ability to cause severe illness in humans. But don't panic just yet; we'll break it all down for you.
Types of Avian Flu
Avian flu isn't a one-size-fits-all kind of deal. There are two main categories:
- Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza (LPAI): This type usually causes mild symptoms in birds and rarely affects humans.
- High Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI): This is the bad boy. It spreads quickly among birds and can cause high mortality rates. It's also the one that occasionally makes the leap to humans.
History of Avian Flu
Avian flu isn't new. The first recorded outbreak of avian influenza in birds occurred way back in Italy in 1878. But it wasn't until the late 20th century that we started seeing cases in humans. The H5N1 strain made headlines in 1997 when it infected humans in Hong Kong for the first time.
Since then, there have been numerous outbreaks across the globe, each one teaching us more about this elusive virus. The history of avian flu is a fascinating journey of discovery, adaptation, and response.
Key Milestones
Let's highlight a few key moments:
Read also:Judge Rules Trumps Fund Block Unconstitutional The Groundbreaking Decision
- 1997: First recorded human infection with H5N1 in Hong Kong.
- 2003-2004: Large outbreaks in Asia, leading to widespread culling of poultry.
- 2013: Emergence of H7N9 in China, a new strain with significant human health implications.
How Does Avian Flu Spread?
Understanding how avian flu spreads is crucial to controlling it. The virus can be transmitted through direct contact with infected birds or their droppings, contaminated surfaces, and even through the air in enclosed spaces.
Wild birds often carry the virus without showing symptoms, making them silent carriers. They can spread the virus over long distances, especially during migration seasons. Domestic birds, on the other hand, are more likely to show symptoms and die from the disease.
Transmission to Humans
The jump from birds to humans is rare but possible. It usually happens through close contact with infected birds or contaminated environments. Activities like handling sick birds, visiting live bird markets, or consuming improperly cooked poultry products can increase the risk.
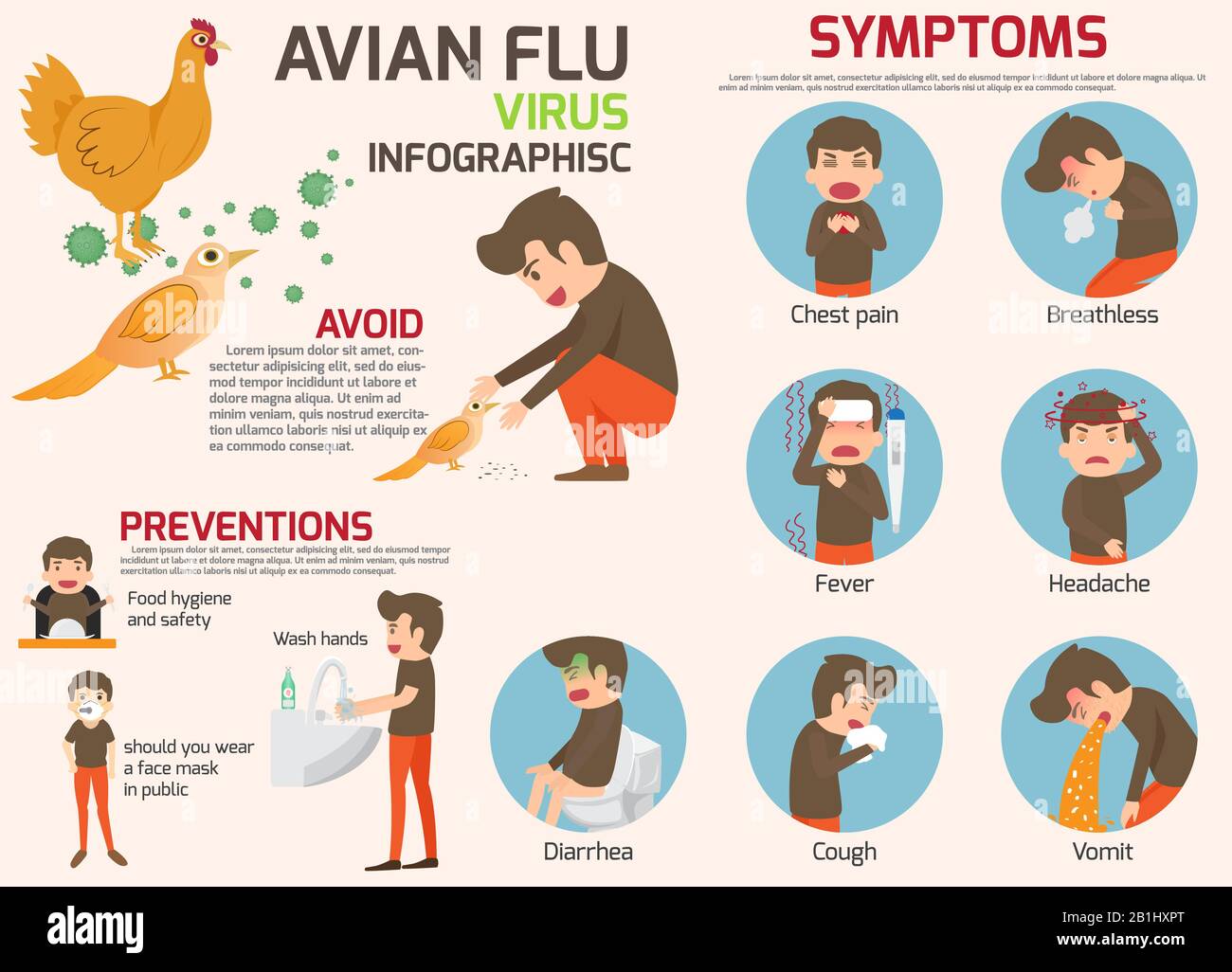
Symptoms of Avian Flu
So, what happens if you get infected with avian flu? The symptoms can vary, but they generally mimic those of regular flu. However, in severe cases, avian flu can lead to life-threatening complications.
Common symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. In more severe cases, patients may experience pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and even multiple organ failure.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing avian flu isn't as simple as taking your temperature. It requires specific laboratory tests to detect the virus in respiratory samples. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and preventing further spread.
Avian Flu in Humans
While avian flu primarily affects birds, its impact on humans is significant. The virus can cause severe illness and has a high mortality rate when it does infect humans. As of now, there's no evidence of sustained human-to-human transmission, but that doesn't mean we can let our guard down.
Most human cases have been linked to direct contact with infected poultry. However, the fear is that the virus could mutate and become more easily transmissible between humans, leading to a potential pandemic.
Risk Factors
Not everyone is equally at risk. People who work closely with poultry, such as farmers and slaughterhouse workers, are more likely to be exposed. Travelers visiting regions with ongoing outbreaks are also at higher risk.
Prevention and Control
Preventing avian flu requires a multi-faceted approach. From vaccination programs for poultry to public health measures, every step counts in controlling the spread of the virus.
Vaccinating poultry can significantly reduce the incidence of avian flu. In some countries, mandatory vaccination programs have been implemented to protect both animal and human populations. For humans, avoiding contact with sick or dead birds and practicing good hygiene are key preventive measures.
Public Health Measures
Governments and health organizations play a crucial role in controlling avian flu outbreaks. Measures such as culling infected flocks, imposing movement restrictions, and monitoring live bird markets are essential tools in the fight against avian flu.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of avian flu is substantial. Outbreaks can lead to massive losses in the poultry industry, affecting livelihoods and food security. Countries with large poultry populations are particularly vulnerable.
Trade restrictions and bans on poultry products can further exacerbate the economic fallout. In some cases, the economic impact extends beyond the poultry sector, affecting related industries such as tourism and agriculture.
Global Economic Losses
Estimates suggest that past avian flu outbreaks have cost the global economy billions of dollars. The loss of poultry alone can be staggering, not to mention the costs associated with containment efforts and compensation for affected farmers.
Global Efforts to Combat Avian Flu
Fighting avian flu is a global effort. International organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) work tirelessly to monitor and control outbreaks. Collaboration between countries is essential to sharing information and resources.
Research into avian flu is ongoing, with scientists working to develop better vaccines and diagnostic tools. Advances in technology are also helping to track the spread of the virus and predict potential outbreaks.
International Cooperation
Global cooperation is key to combating avian flu. Sharing data, resources, and expertise can lead to more effective prevention and control strategies. It's a battle we can win if we work together.
Recent Outbreaks
Avian flu isn't just a thing of the past. Recent outbreaks have been reported in various parts of the world, underscoring the ongoing threat posed by this virus. In 2022 and 2023, there were significant outbreaks in Europe, Asia, and North America.
These outbreaks have highlighted the need for continued vigilance and improved surveillance systems. They serve as a reminder that avian flu is a global health issue that demands our attention and action.
Lessons Learned
Each outbreak teaches us valuable lessons. From improving early detection systems to enhancing preparedness plans, we're constantly learning and adapting to better combat avian flu.
Conclusion
So, there you have it—the lowdown on avian flu. From its origins and spread to its impact on both animals and humans, we've covered a lot of ground. The key takeaway is that avian flu is a serious global health concern that requires our attention and action.
Here's what you can do: stay informed, practice good hygiene, and support efforts to control and prevent avian flu. Together, we can make a difference. So, what are you waiting for? Share this article, leave a comment, and let's keep the conversation going.
Remember, knowledge is power. The more we know about avian flu, the better equipped we are to face it. Let's continue to learn, adapt, and protect ourselves and our planet from this ever-evolving threat.